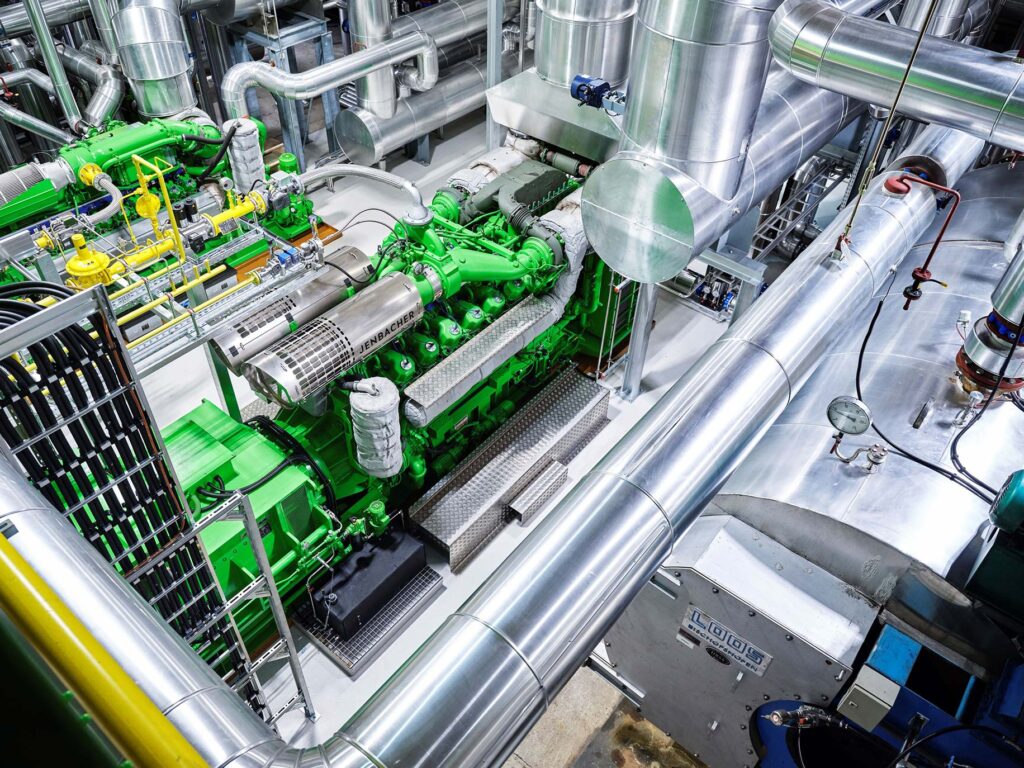
As a hydrogen pioneer, INNIO Group has been working with the CO2-free energy source for more than 30 years. However, a major challenge when developing engines that run on hydrogen is securing a sufficient supply of green hydrogen (H2).

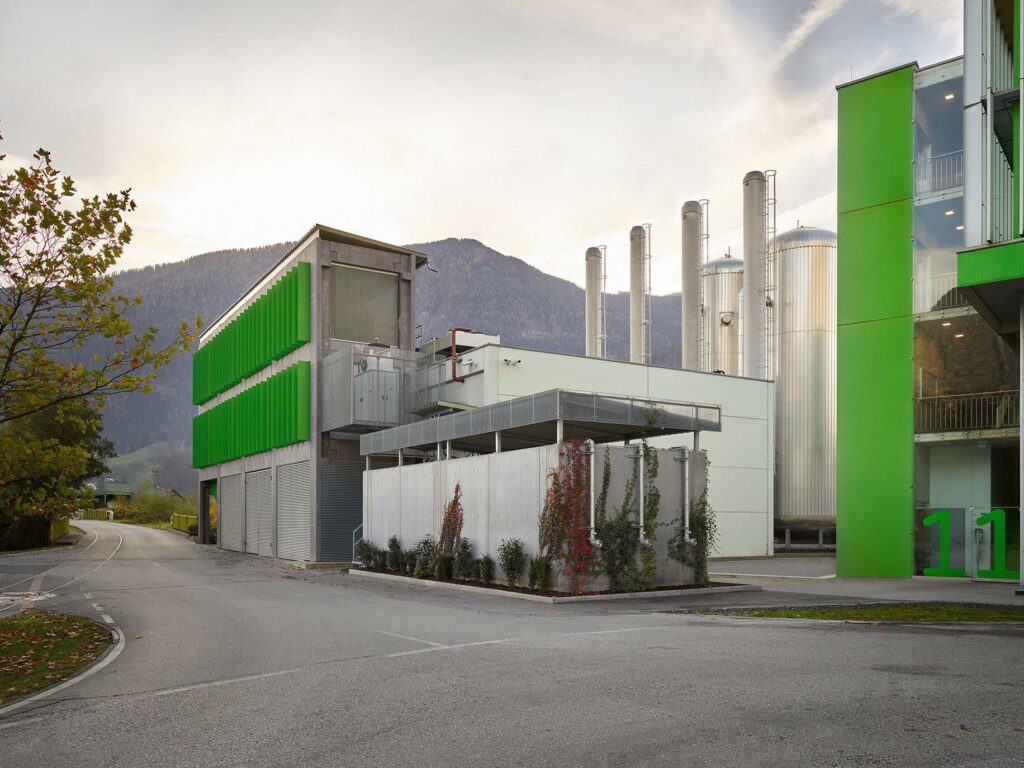
Beginning in 2025, INNIO has secured a constant supply of hydrogen for its primary operation in Jenbach via a direct line from a local energy supplier. An important step in implementing the Group’s sustainable hydrogen product strategy, the supply of green hydrogen at the Jenbach site is also a milestone on the way toward climate neutrality there.
2025
220 metric tons H2
every year for Jenbacher test benches
1,000 kg/h
2040
climate neutrality target
Progress in developing highly efficient hydrogen engines takes more than a commitment to innovation, many years of expertise, and in-depth technical knowledge. It also depends on a sufficient supply of hydrogen. The problem is that green hydrogen – an environmentally friendly energy source that is key to the energy transformation – is still rare. A Jenbacher J620 engine with an average output of 2.7 MW consumes 200 kg of H2 in an hour. A Jenbacher J920 FleXtra with an average output of 7.8 MW, meanwhile, needs 580 kg of H2 each hour. H2 trailer solutions simply cannot supply enough hydrogen. With a capacity between 250 kg and 500 kg, the trailer solutions struggle to support a test run for an hour, which is just not enough to keep on developing this engine technology. In response to this situation, INNIO signed an agreement with a local energy supplier to ensure a constant and sufficient supply of H2 to its primary operation in Jenbach. Initially, a 2 MW electrolyzer will supply the Jenbacher test benches with about 220 metric tons of hydrogen a year, and plans call for tripling the H2 production capacity to 6 MW. The storage capacity will begin at 1,000 kg per hour.
Hydrogen Summit Live Broadcast
To use Youtube, please give your consent to the creation of cookies used by this service.

Vision of Energy Supply Without CO2
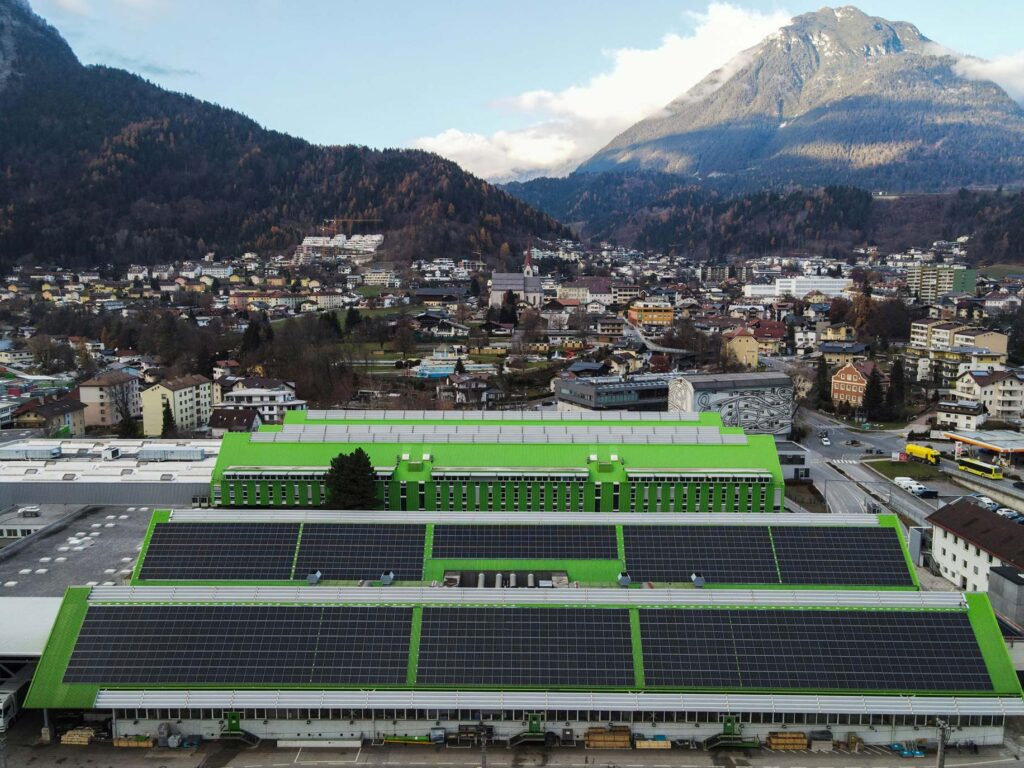
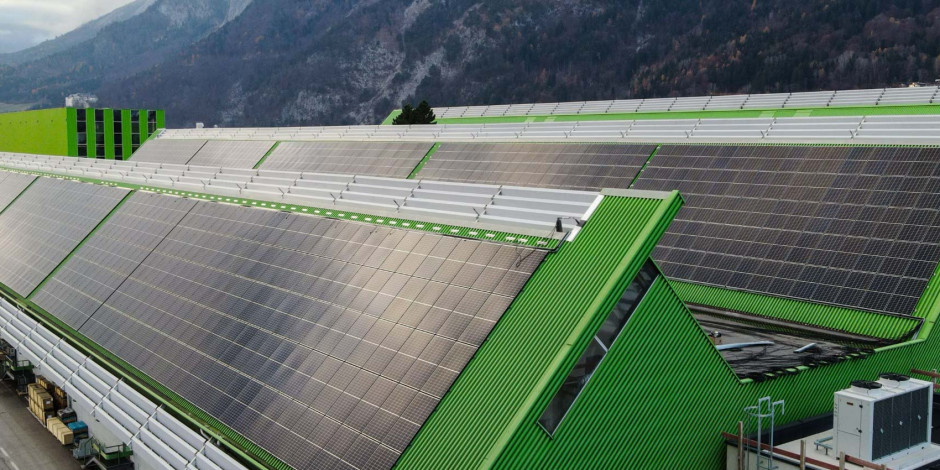
INNIO uses its own energy management system from the myPlant digital platform at its INNIO360 Energy Lab. Located at the main production site in Jenbach, the INNIO360 Energy Lab includes a photovoltaic (PV) plant and an intelligent energy storage system, optimized with INNIO’s microgrid control solutions. In the microgrid, all test benches are integrated and controlled with the myPlant energy management system for economical management. In the future, H2, biogas, and special gases will be the primary energy sources used for test runs on Jenbacher engines alongside pipeline gas. The field test engines and the boiler in the INNIO360 Energy Lab also are being converted into a dual gas system (H2/pipeline gas) to enable the use of CO2-free energy sources (in addition to photovoltaics, hydropower, power-to-heat using electricity from the grid, and heat storage tanks). The waste heat from the test benches connected to heat technology and the heat converted via power-to-heat and from H2 production are being used in the factory itself and subsequently will be fed into the district heating network. The power generated at the test benches meets the site’s demands and is converted into heat to be stored. Any excess energy is fed into the public grid. INNIO is confident that this strategic approach has the potential to lead to climate neutrality at the Jenbach site – and will set a shining example of how the energy transition can be implemented in the process.
We need to see a fundamental shift in our global energy system. Here in Jenbach, we’re demonstrating how to achieve climate neutrality.
Rudolf Raunig, director of Infrastructure for INNIO Group at the Jenbach site